If Ubuntu Linux does not boot correctly on your PC, this document can help you correct the problem by troubleshooting through Ubuntu's recovery mode, troubleshooting through a boot-repair CD, or by updating the display driver.
If you have installed only Ubuntu, you have a single-operating-system (single-OS) PC. If you have also installed at least one other OS, such as Linux Mint and/or MS Windows, you have a multiboot PC.
Note: The procedures in this document primarily apply to PCs that were built before 2011. Therefore, if your PC was built since 2010, booting more than one OS is difficult due to the Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI). For more information, please see Ubuntu Documentation - UEFI.
Troubleshooting Through Recovery Mode
After opening the GRand Universal Bootloader (GRUB) menu, you can troubleshoot an Ubuntu boot problem through the Recovery mode, which lets you repair broken packages and, if necessary, check all file systems.
Opening the GRUB Menu - How you open the GRUB menu varies according to whether you have installed Ubuntu on a single-OS or a multiboot PC:
- For Ubuntu on a Single-OS PC, open the GRUB menu according to the procedure on the Ubuntu wiki Recovery Mode web page.
- For Ubuntu on a multiboot PC, starting or restarting that PC opens a GRUB menu that lets you select an OS to boot.
Repairing Broken Packages - Repairing broken packages might correct an Ubuntu boot problem. To repair broken packages, do the following:
- Open GRUB according to the Opening the GRUB Menu section above.
- As shown in Figure 1 below, highlight Ubuntu - - Recovery Mode, and then press Enter to boot in Recovery mode.
- As shown in Figure 2 below, highlight dpkg _ _ Repair broken packages, press Enter, and then follow the prompts to repair the packages.
- Use the Testing Ubuntu Boot section below to test whether you have repaired the Ubuntu boot problem.
Checking All File Systems - Checking all file systems might correct an Ubuntu boot problem. To check all file systems, do the following:
- Open GRUB according to the Opening the GRUB Menu section above.
- As shown in Figure 1 below, highlight Ubuntu - - Recovery Mode, and then press Enter to boot in Recovery mode.
- Highlight fsck _ _ Check all file systems, press Enter, and then follow the prompts to check the file systems.
- Use the Testing Ubuntu Boot section below to test whether you have repaired the Ubuntu boot problem.
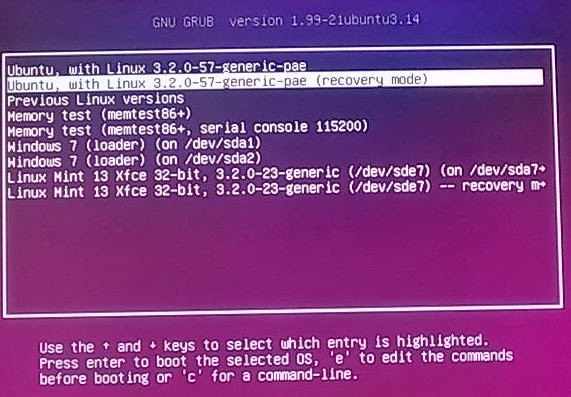 |
| Figure 1 - Selecting Ubuntu Recovery Mode |
 |
| Figure 2 - Repairing Broken Packages |
Troubleshooting Through a Boot Repair CD
You can use a boot repair CD to find and correct many Ubuntu boot problems. To troubleshoot through a boot-repair CD, do the following:
- Burn the ISO file onto a blank CD to create a boot-repair CD.
- Boot your PC through your boot-repair CD.
- When prompted, click Recommended repair, and then follow the prompts.
- Use the Testing Ubuntu Boot section below to test whether you have repaired the Ubuntu boot problem.
Updating the Display Driver
An outdated display driver can cause Ubuntu to boot incorrectly and/or intermittently. To update to the newest display driver, do the following:
- In the Launcher, click the System Settings icon.
- In the Hardware frame, click Additional Drivers to display its window.
- Wait while Ubuntu searches for drivers, and then displays the Additional Drivers window.
- As shown in Figure 3 below, select the newest possible display driver. For example, in Ubuntu 12.04, you could select "NVIDIA accelerated graphics driver (post-release updates) (version 304-updates)."
- Use the Testing Ubuntu Boot section below to test whether you have repaired the Ubuntu boot problem.
 |
| Figure 3 - Selecting the Newest Possible Display Driver |
Testing Ubuntu Boot
After troubleshooting Ubuntu boot through any section above, you need to test whether Ubuntu boots correctly. To test Ubuntu boot, do the following:
- Shut down your PC.
- Wait at least 15 seconds.
- Start your PC.
- Boot Ubuntu. If it does not boot correctly, continue troubleshooting through any other appropriate section above. Note: In case this document has not helped, you can check Ubuntu Support.