Tkinter is the most popular graphical user interface (GUI) for the Python programming language. Tkinter automatically installs with Python. This document describes example code through which you can create a new desktop window that contains active buttons and dynamic labels.
I thank Webucator for creating an excellent video presentation based on this document, and including it in a free lesson, Python Solutions from the Web. Webucator also provides commercial Python Online and Onsite Training Classes.
Example GUI overview
Figjures 1, 2 and 3 contain the example GUI example code. Note: In these figures, # characters precede red comment text that shows how Tkinter widgets define these example buttons and labels.
 |
| Figure 1 - This code defines the Button Test window, its instruction text, and its Exit Program button. |
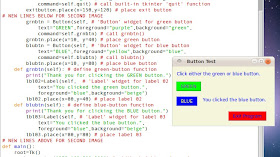 |
| Figure 2 - This code defines the GREEN and BLUE buttons. |
 |
| Figure 3 - This code defines the Reset button. |
To download and then run the example GUI, do the following:
- In a new browser window or tab, go to Tkinter Buttons and Labels.
- Select the entire program, and then press Ctrl+C to copy the code.
- Start Python 3 and open a new window in IDLE.
- Click File, click New File, and then press Ctrl+V to paste your copied code into your new file.
- Save your new file with an appropriate file name, such as TkinterExample.py, and then click Run Module.
- Test the buttons according to the Testing the example GUI section below.
If you are new to Python, you might wish to type the example GUI as extra practice. To type and run the example GUI, do the following:
- Start Python 3 and open a new window in IDLE.
- Click File, click New File, and then type the code from Figures 1, 2, and 3 into your new file.
- Save your new file with an appropriate file name, such as TkinterExample.py, and then click Run Module.
- Test the buttons according to the Testing the example GUI section below.
After downloading or typing the example GUI, test it as follows:
- Click the GREEN button to display "You clicked the green button" in its label field.
- Click the BLUE button to display "You clicked the blue button."
- Click the RESET button should clear the label fields for the GREEN and BLUE buttons.
- Repeat steps 1 through 3 to verify that the print() functions display correctly in the Python Shell. For example, clicking the BLUE button should also display "Thank you for clicking the BLUE button" as shown in Figure 4.
- Click the Exit Program button to close the Button Test window.
 |
| Figure 4 - Clicking the BLUE button should display one message in the Button Test window, and another in the Python Shell window. |
No comments :
Post a Comment